Cheat Sheet
This cheat sheet describes the essential APIs that are commonly used. For the complete list of the API, see the API reference.
Overview
General
ebiten.Game
type Game interface {
// Update updates a game by one tick.
Update() error
// Draw draw the game screen. The given argument represents a screen image.
Draw(screen *Image)
// Layout accepts a native outside size in device-independent pixels and returns the game's logical
// screen size. On desktops, the outside is a window or a monitor (fullscreen mode)
//
// Even though the outside size and the screen size differ, the rendering scale is automatically
// adjusted to fit with the outside.
//
// You can return a fixed screen size if you don't care, or you can also return a calculated screen
// size adjusted with the given outside size.
Layout(outsideWidth, outsideHeight int) (screenWidth, screenHeight int)
}Game defines necessary functions for a game.
ebiten.RunGame
func RunGame(game Game) errorRunGame runs the game. game's Update is called every tick (1/60 [s] by default) and game's Draw is called every frame (typically 1/60[s] for 60Hz display). The argument (*Image) is the render target that represents the screen.
The Update and the Draw are not called when the window is unfocused by default. This setting is configurable with SetRunnableOnUnfocused.
RunGame returns error when 1) OpenGL error happens, 2) audio error happens or 3) f returns error. In the case of 3), RunGame returns the same error.
Don't call RunGame twice or more in one process.
The typical code with Game and RunGame is this:
// Game implements ebiten.Game interface.
type Game struct{}
// Update proceeds the game state.
// Update is called every tick (1/60 [s] by default).
func (g *Game) Update() error {
// Write your game's logical update.
return nil
}
// Draw draws the game screen.
// Draw is called every frame (typically 1/60[s] for 60Hz display).
func (g *Game) Draw(screen *ebiten.Image) {
// Write your game's rendering.
}
// Layout takes the outside size (e.g., the window size) and returns the (logical) screen size.
// If you don't have to adjust the screen size with the outside size, just return a fixed size.
func (g *Game) Layout(outsideWidth, outsideHeight int) (screenWidth, screenHeight int) {
return 320, 240
}
func main() {
game := &Game{}
// Specify the window size as you like. Here, a doubled size is specified.
ebiten.SetWindowSize(640, 480)
ebiten.SetWindowTitle("Your game's title")
// Call ebiten.RunGame to start your game loop.
if err := ebiten.RunGame(game); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}ebiten.Run
Run is for backward compatibility and was replaced with RunGame.
ebitenutil.DebugPrint
func DebugPrint(image *ebiten.Image, str string)(Defined at ebitenutil package)
DebugPrint draws the string str on the image on left top corner.
DebugPrint always returns nil.
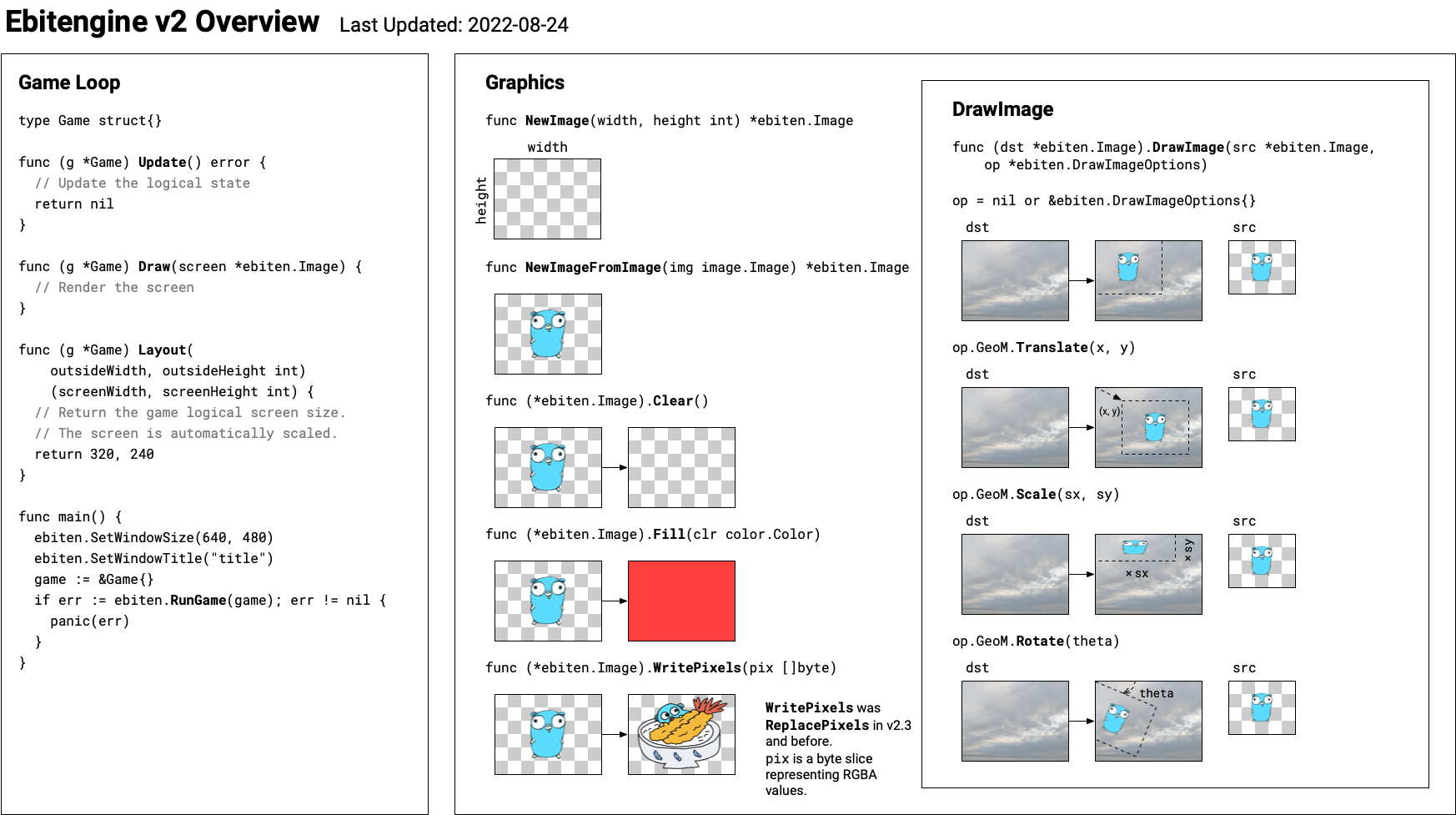
Graphics
ebiten.Image
type Image struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}Image represents a rectangle set of pixels. The pixel format is alpha-premultiplied RGBA. Image implements image.Image.
ebiten.NewImage
func NewImage(width, height int) *ImageNewImage returns an empty image.
ebiten.NewImageFromImage
func NewImageFromImage(source image.Image) *ImageNewImageFromImage creates a new image with the given image (source).
(*ebiten.Image).Clear
func (i *Image) Clear()Clear resets the pixels of the image into 0.
(*ebiten.Image).Fill
func (i *Image) Fill(clr color.Color)Fill fills the image with a solid color.
(*ebiten.Image).Size
func (i *Image) Size() (width, height int)Size returns the size of the image.
(*ebiten.Image).SubImage
func (i *Image) SubImage(r image.Rectangle) image.ImageSubImage returns an image representing the portion of the image p visible through r. The returned value shares pixels with the original image.
The returned value is always *ebiten.Image.
If the image is disposed, SubImage returns nil.
In the current Ebitengine implementation, SubImage is available only as a rendering source.
(*ebiten.Image).DrawImage
func (i *Image) DrawImage(img *Image, options *DrawImageOptions)DrawImage draws the given image on the image i.
DrawImage accepts the options. For details, see the document of DrawImageOptions.
DrawImage determines the part to draw, then DrawImage applies the geometry matrix and the color matrix.
For drawing, the pixels of the argument image at the time of this call is adopted. Even if the argument image is mutated after this call, the drawing result is never affected.
When the given image is as same as i, DrawImage panics.
DrawImage works more efficiently as batches when the successive calls of DrawImages satisfies the below conditions:
- All render targets are same (
AinA.DrawImage(B, op)) - Either all ColorM element values are same or all the ColorM have only diagonal ('scale') elements
- If only
(*ColorM).Scaleis applied to a ColorM, the ColorM has only diagonal elements. The other ColorM functions might modify the other elements.
- If only
- All CompositeMode values are same
- All Filter values are same
For more details, see Performance Tips.
ebiten.DrawImageOptions
type DrawImageOptions struct {
// GeoM is a geometry matrix to draw.
// The default (zero) value is identify, which draws the image at (0, 0).
GeoM GeoM
// ColorM is a color matrix to draw.
// The default (zero) value is identity, which doesn't change any color.
ColorM ColorM
// CompositeMode is a composite mode to draw.
// The default (zero) value is regular alpha blending.
CompositeMode CompositeMode
// Filter is a type of texture filter.
// The default (zero) value is FilterNearest.
Filter Filter
}DrawImageOptions represents options to render an image on an image.
ebiten.Filter
type Filter intFilter represents the type of texture filter to be used when an image is maginified or minified.
const (
// FilterNearest represents nearest (crisp-edged) filter
FilterNearest
// FilterLinear represents linear filter
FilterLinear
)ebiten.GeoM
type GeoM struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}GeoM represents a matrix to transform geometry when rendering an image.
The initial value is identity.
(*ebiten.GeoM).Translate
func (g *GeoM) Translate(tx, ty float64)Translate translates the matrix by (tx, ty).
(*ebiten.GeoM).Scale
func (g *GeoM) Scale(x, y float64)Scale scales the matrix by (x, y).
(*ebiten.GeoM).Rotate
func (g *GeoM) Rotate(theta float64)Rotate rotates the matrix by theta. The unit is radian.
ebiten.ColorM
type ColorM struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}ColorM represents a matrix to transform coloring when rendering an image.
ColorM is applied to the straight alpha color while an Image's pixels' format is alpha premultiplied. Before applying a matrix, a color is un-multiplied, and after applying the matrix, the color is multiplied again.
The initial value is identity.
(*ebiten.ColorM).Scale
func (c *ColorM) Scale(r, g, b, a float64)Scale scales the matrix by (r, g, b, a).
(*ebiten.ColorM).Translate
func (c *ColorM) Translate(r, g, b, a float64)Translate translates the matrix by (r, g, b, a).
(*ebiten.ColorM).ChangeHSV
func (c *ColorM) ChangeHSV(hueTheta float64, saturationScale float64, valueScale float64)ChangeHSV changes HSV (Hue-Saturation-Value) values. hueTheta is a radian value to rotate hue. saturationScale is a value to scale saturation. valueScale is a value to scale value (a.k.a. brightness).
Input
ebiten.IsKeyPressed
func IsKeyPressed(key Key) boolIsKeyPressed returns a boolean indicating whether key is pressed.
inpututil.IsKeyJustPressed
func IsKeyJustPressed(key ebiten.Key) bool(Defined at inpututil package)
IsKeyJustPressed returns a boolean value indicating whether the given key is pressed just in the current frame.
ebiten.Key
type Key intKey represents a keyboard key. These keys represent pysical keys of US keyboard. For example, KeyQ represents Q key on US keyboards and ' (quote) key on Dvorak keyboards.
const (
KeyA Key
KeyB
KeyC
KeyD
KeyE
KeyF
KeyG
KeyH
KeyI
KeyJ
KeyK
KeyL
KeyM
KeyN
KeyO
KeyP
KeyQ
KeyR
KeyS
KeyT
KeyU
KeyV
KeyW
KeyX
KeyY
KeyZ
KeyAltLeft
KeyAltRight
KeyArrowDown
KeyArrowLeft
KeyArrowRight
KeyArrowUp
KeyBackquote
KeyBackslash
KeyBackspace
KeyBracketLeft
KeyBracketRight
KeyCapsLock
KeyComma
KeyContextMenu
KeyControlLeft
KeyControlRight
KeyDelete
KeyDigit0
KeyDigit1
KeyDigit2
KeyDigit3
KeyDigit4
KeyDigit5
KeyDigit6
KeyDigit7
KeyDigit8
KeyDigit9
KeyEnd
KeyEnter
KeyEqual
KeyEscape
KeyF1
KeyF2
KeyF3
KeyF4
KeyF5
KeyF6
KeyF7
KeyF8
KeyF9
KeyF10
KeyF11
KeyF12
KeyHome
KeyInsert
KeyMetaLeft
KeyMetaRight
KeyMinus
KeyPageDown
KeyPageUp
KeyPause
KeyPeriod
KeyPrintScreen
KeyQuote
KeyScrollLock
KeySemicolon
KeyShiftLeft
KeyShiftRight
KeySlash
KeySpace
KeyTab
KeyAlt
KeyControl
KeyShift
KeyMeta
)(Note: Some keys like numpad keys are omitted from the above list.)
ebiten.CursorPosition
func CursorPosition() (x, y int)CursorPosition returns a position of a mouse cursor.
ebiten.IsMouseButtonPressed
func IsMouseButtonPressed(mouseButton MouseButton) boolIsMouseButtonPressed returns a boolean indicating whether mouseButton is pressed.
inpututil.IsMouseButtonJustPressed
func IsMouseButtonJustPressed(button ebiten.MouseButton) bool(Defined at inpututil package)
IsMouseButtonJustPressed returns a boolean value indicating whether the given mouse button is pressed just in the current frame.
ebiten.MouseButton
type MouseButton intMouseButton represents a mouse button.
const (
MouseButtonLeft MouseButton
MouseButtonRight
MouseButtonMiddle
)